Unlocking The Secrets Of The Mediterranean Diet: A Deep Dive Into Greek Nutrition
The Mediterranean diet has been hailed as one of the healthiest diets in the world, and for good reason. This ancient eating pattern, inspired by the traditional diets of Greece and other Mediterranean countries, has been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer. At its core, the Mediterranean diet is about simplicity, freshness, and whole foods, emphasizing locally sourced ingredients and traditional cooking methods. By understanding the secrets of the Mediterranean diet, you can unlock a healthier, happier you.
The Mediterranean diet is not just a diet, it's a lifestyle. It's about savoring food, sharing meals with loved ones, and enjoying the company of others. It's about taking time to appreciate the simple things in life, like a perfectly ripe tomato or a crusty loaf of bread. When you adopt a Mediterranean diet, you're not just eating for yourself, you're eating for your community and your heritage.
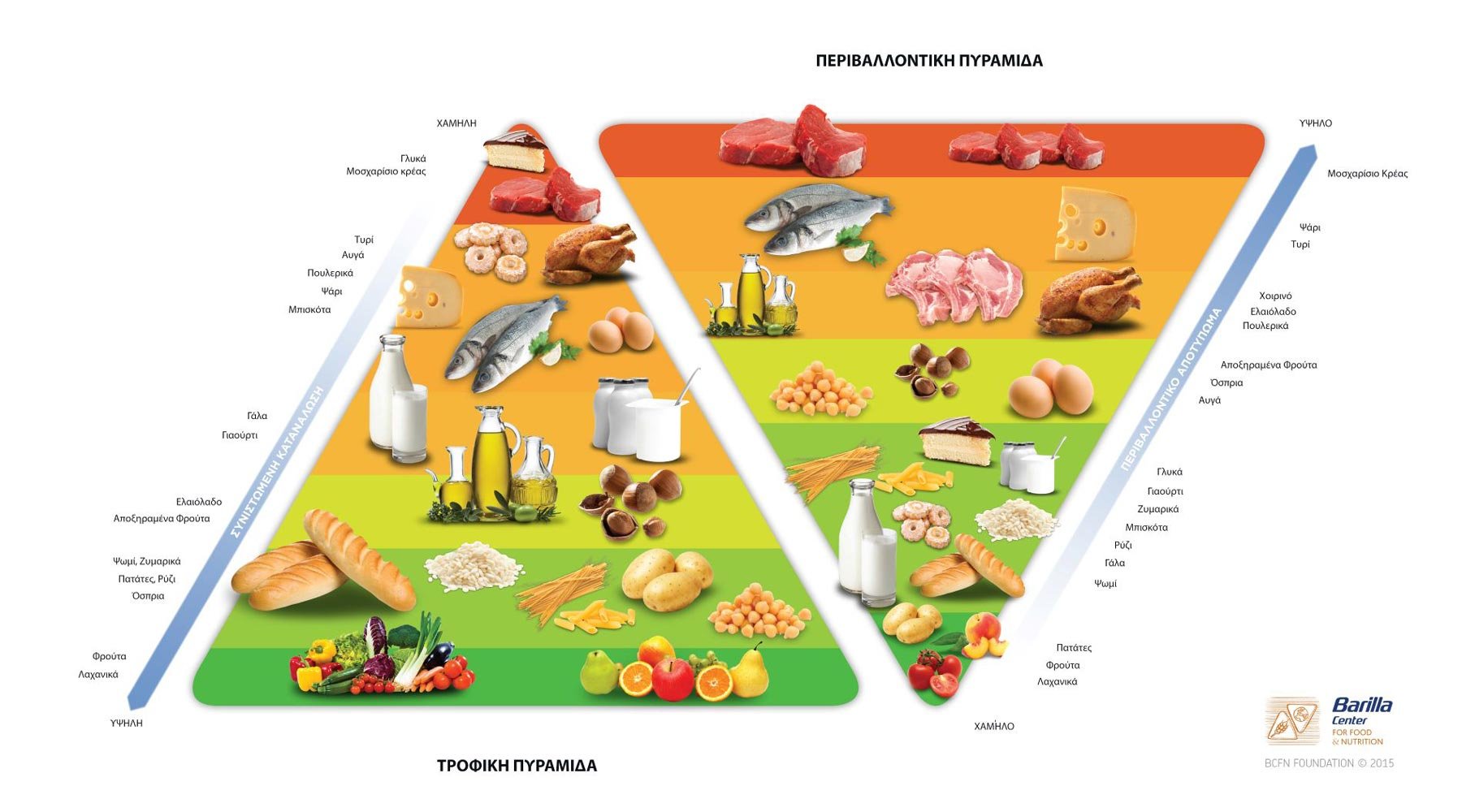
One of the key principles of the Mediterranean diet is its emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods. This means no packaged snacks, no sugary drinks, and no fast food. Instead, focus on whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, along with an array of colorful vegetables, fresh fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats. By eating more whole foods, you'll be reducing your intake of unhealthy additives, preservatives, and excessive salt.
Some of the key foods that make up the Mediterranean diet include:
- Olive oil: the star of the Mediterranean diet
- Leafy greens: like spinach, kale, and collard greens
- Legumes: like lentils, chickpeas, and fava beans
- Fatty fish: like salmon, tuna, and sardines
- Whole grains: like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread
- Herbs and spices: like oregano, thyme, and rosemary
History of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet has its roots in ancient Greece, where it was known as the "Kalorikon Diet". This diet was popularized by the Greek physician Hippocrates, who believed that a diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains could cure a wide range of ailments. The diet was also influenced by the traditional diets of other Mediterranean countries, such as Italy, Spain, and Turkey.
In the 1950s and 60s, the Mediterranean diet began to gain popularity in the United States, where it was studied by scientists like Ancel Keys and Frank Sacks. These researchers were fascinated by the diet's health benefits and began to investigate its effects on heart disease, cancer, and other chronic diseases.
Key Components of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is not a one-size-fits-all approach to eating. Instead, it's a flexible framework that allows you to make healthy choices based on your individual needs and preferences. Here are some key components of the Mediterranean diet:
- High consumption of fruits and vegetables: aim for at least five servings a day
- High consumption of whole grains: choose whole grains over refined grains
- High consumption of lean protein sources: like poultry, fish, and legumes
- High consumption of healthy fats: like olive oil, avocado, and nuts
- Moderate consumption of dairy products: like yogurt, cheese, and milk
- Low consumption of red meat: limit your intake of red meat to once or twice a week

How to Incorporate the Mediterranean Diet into Your Life
Incorporating the Mediterranean diet into your life doesn't have to be overwhelming. Here are some simple tips to get you started:
- Start with small changes: try adding one or two new ingredients to your meals each week
- Explore new recipes: find healthy, delicious recipes online or in cookbooks
- Make healthy swaps: choose whole grains over refined grains, and opt for lean protein sources
- Drink plenty of water: aim for at least eight glasses a day
- Savor your food: take time to enjoy your meals, and appreciate the company of others
Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including:
- Reducing the risk of heart disease: by lowering cholesterol and blood pressure
- Reducing the risk of stroke: by improving circulation and preventing blood clots
- Reducing the risk of certain cancers: like breast, colon, and prostate cancer
- Improving cognitive function: by reducing the risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease
- Promoting weight loss: by reducing calorie intake and increasing satiety
Common Challenges to Adopting the Mediterranean Diet
While the Mediterranean diet is a simple, healthy approach to eating, there are some common challenges to adopting it:
- Cultural or social barriers: like trying new foods or adjusting to new eating habits
- Limited access to healthy foods: like fresh produce or lean protein sources
- Time constraints: like finding time to cook and prepare meals
- Budget constraints: like affording healthy groceries
- Nutritional deficiencies: like ensuring adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals
Tips for Eating Like a Greek
To eat like a Greek, try the following tips:
- Use fresh, locally sourced ingredients: like lemons, olives, and fresh herbs
- Cook with olive oil: like olive oil is a staple of Greek cuisine
- Eat whole grains: like whole wheat bread, brown rice, and quinoa
- Include a variety of vegetables: like bell peppers, eggplant, and zucchini
- Add healthy fats: like feta cheese, avocado, and nuts
Greek Superfoods
Greece is famous for its superfoods, including:
Clintastwoodndorsement 2024
Quiero Agua
Is Till Alive
Article Recommendations
- Borisanchez Wife
- Ge Clooney Children
- Blowout R With Curly Hair
- Original Beyblade
- Pabloe Morale
- Naples Pier Cam Live
- Adamell
- Whatoes Eminem Look Like Now
- Melissaerosa Net Worth
- Simon Cowellonownyndrome