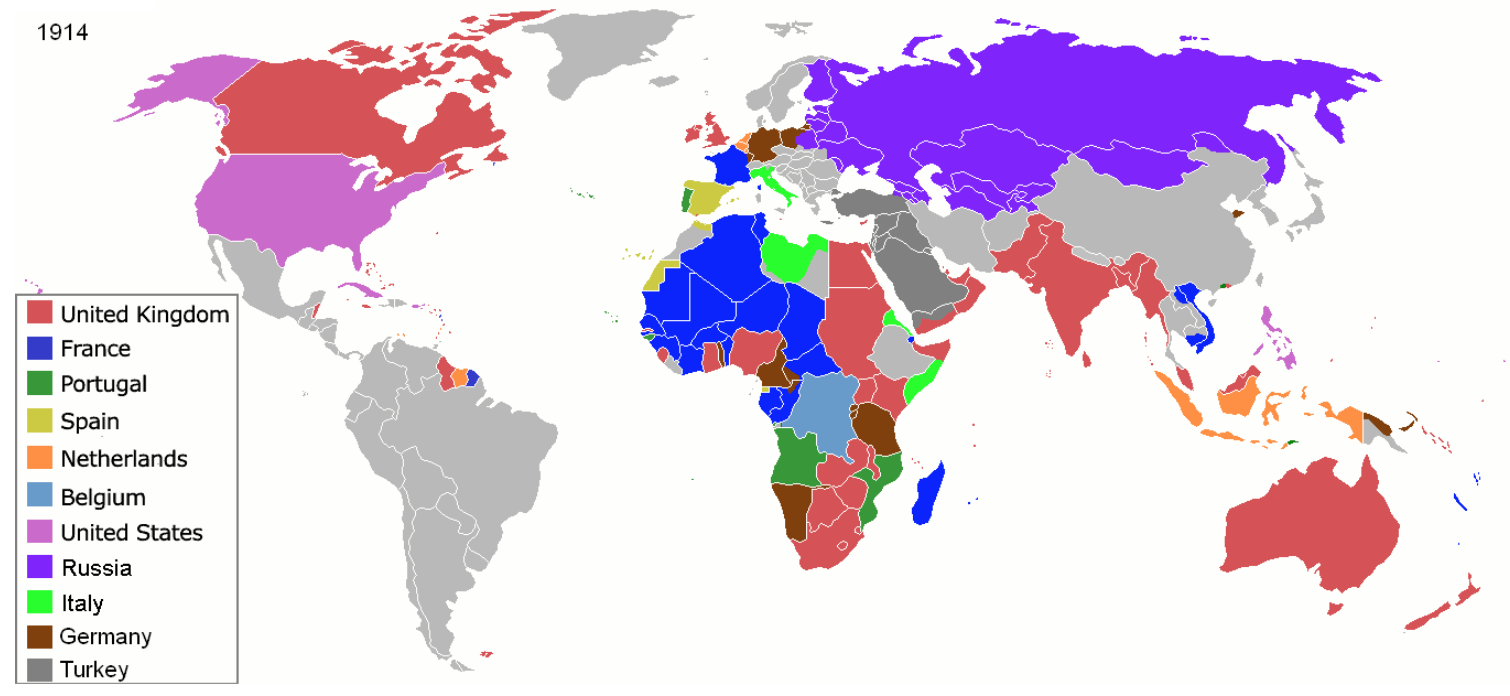
Mapping Empire: A Visual Journey Through Imperialism's History
The history of imperialism is a complex and multifaceted topic that has shaped the world as we know it today. From the ancient empires of Egypt and Rome to the modern-day global powers, imperialism has played a significant role in the development of human civilization. In this article, we will embark on a visual journey through the history of imperialism, exploring its causes, effects, and legacy.
Imperialism is often defined as the extension of a country's power and influence through colonization, conquest, or other means. This definition encompasses a wide range of activities, from the trading posts of the Renaissance to the colonial empires of the 19th and 20th centuries. As we explore the history of imperialism, we will see how different empires and powers have used various strategies to expand their territories and exert their control over other regions.
Imperialism is not a new phenomenon, but rather a recurring theme throughout human history. Many ancient civilizations, including the Babylonians, Assyrians, and Persians, expanded their empires through conquest and colonization. The ancient Greeks and Romans also established extensive empires that lasted for centuries. However, it was not until the Age of Exploration that imperialism began to take on its modern form, with European powers establishing colonies and trading posts around the world.
Causes of Imperialism
Imperialism is often driven by a combination of economic, military, and strategic factors. One of the primary drivers of imperialism is the desire for natural resources, such as gold, silver, and other precious commodities. European powers, in particular, sought to establish colonies in regions rich in these resources, which helped to fuel their industrial revolutions and economic growth.
Economic Factors
- The desire for natural resources and trade routes
- The need for raw materials to fuel industrialization
- The establishment of new markets and trade routes
For example, the British Empire's colonization of India in the 18th century was driven in part by the desire for Indian cotton, which was used to fuel the British textile industry. Similarly, the German Empire's colonization of Africa in the late 19th century was motivated by a desire to establish new markets for German goods and to secure access to African resources.
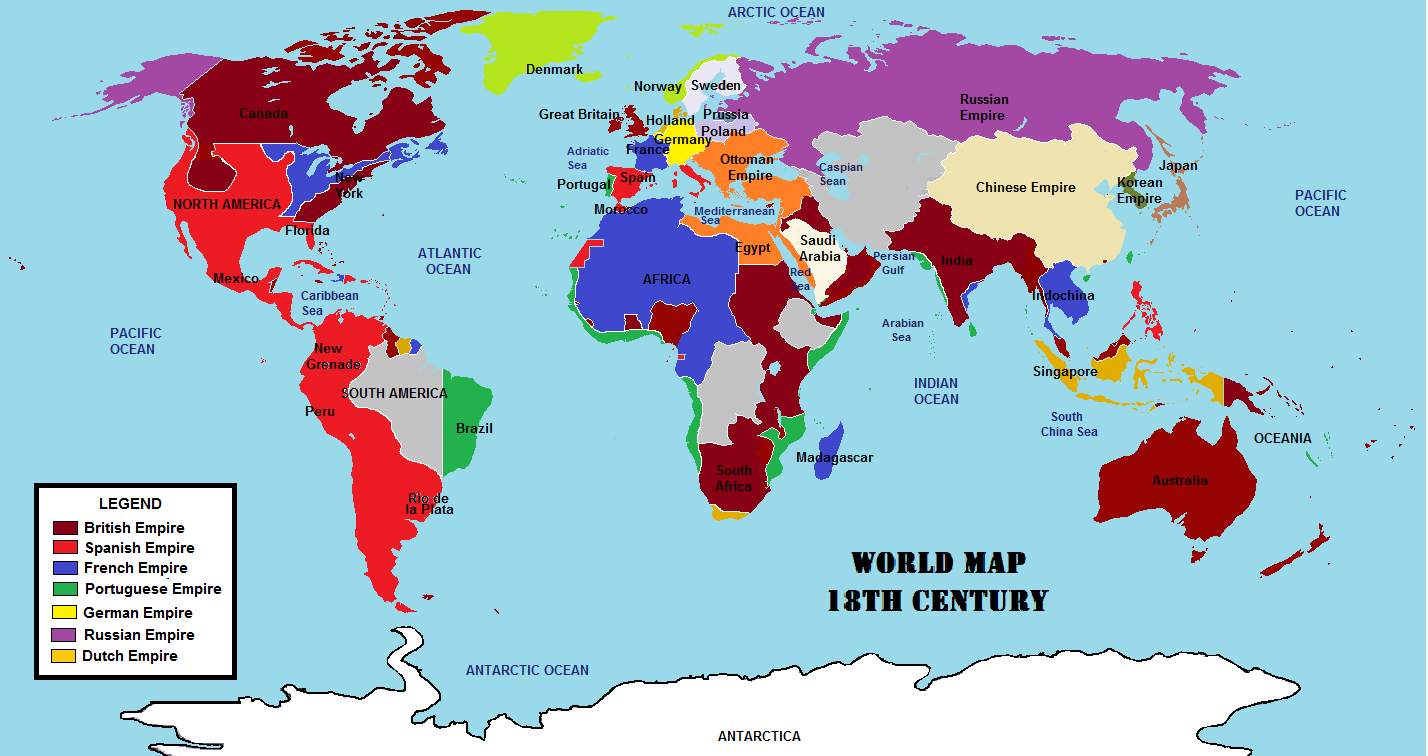
Military Factors
- The need for strategic military bases and outposts
- The desire to protect trade routes and commerce
- The establishment of military occupations and protectorates
The British Empire, for example, established a network of military outposts and bases across its colonies, which helped to maintain control and protect trade routes. Similarly, the German Empire's military campaigns in Africa and Asia were motivated by a desire to establish strategic military bases and secure access to resources.
Strategic Factors
- The need for strategic alliances and treaties
- The desire to project power and influence globally
- The establishment of colonial administration and governance
Imperialism is also driven by strategic factors, including the need for alliances and treaties with other powers. European powers, for example, formed the Concert of Europe in the 19th century, which helped to maintain stability and prevent conflict in Europe. Similarly, the British Empire established a network of colonial administrations and governance structures, which helped to maintain control and stability in its colonies.
Effects of Imperialism
Imperialism has had a profound impact on the world, shaping global politics, economies, and cultures in profound ways. Some of the key effects of imperialism include:
Economic Effects
- The transfer of wealth and resources from colonized to colonizer
- The establishment of new economic systems and institutions
- The exploitation of local labor and resources
Imperialism has also had a profound impact on the global economy, with many colonized countries struggling to develop their own economies and industries. The transfer of wealth and resources from colonized to colonizer has also had a profound impact on the global economy, with many countries relying on the wealth generated by their colonies to fuel their own economic growth.
Social Effects
- The displacement and marginalization of indigenous populations
- The establishment of new social systems and institutions
- The exploitation of local labor and resources
Imperialism has also had a profound impact on social structures, with many indigenous populations being displaced and marginalized by the arrival of colonizers. The establishment of new social systems and institutions has also had a profound impact on local cultures and identities.

Cultural Effects
- The suppression of local cultures and languages
- The imposition of foreign values and institutions
- The exchange of ideas and cultures
Imperialism has also had a profound impact on culture, with many local cultures and languages being suppressed or imposed by the colonizers. However, imperialism has also facilitated the exchange of ideas and cultures, with many colonized countries adopting foreign values and institutions.
Legacy of Imperialism
Imperialism has left a lasting legacy on the world, shaping global politics, economies, and cultures in profound ways. Some of the key legacies of imperialism include:
Political Legacies
- The establishment of new nation-states and borders
- The creation of international systems and institutions
- The shaping of global governance and politics
Imperialism has also had a profound impact on global governance and politics, with many international systems and institutions being established to manage the legacy of colonialism. The creation of new nation-states and borders has also had a profound impact on global politics, with many countries emerging from colonialism as independent nations.
Economic Legacies
- The creation of global trade systems and networks
- The establishment of new economic institutions and systems
- The shaping of global economic structures
Imperialism has also had a profound impact on global economic structures, with many economic institutions and systems being established to manage the legacy of colonialism. The creation of global trade systems and networks has also had a profound impact on global commerce, with many countries relying on trade with other nations to fuel their economic growth.
Cultural Legacies
- The
Michael Keatonson
Anthony Kiedis Wife Age
Kat All
Article Recommendations
- Sammy Hagar Young
- Natane Adcock Husband
- Actor Bobby Cannavale
- All American
- Vex Incursion Zone
- Steamhouse Midtown
- Brittany Mahomesupports Husband Patrick At Chiefs Game With Children
- Money6x Earning
- Justin Qualley
- Hugh Grant Autist